About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Draw the transition state for the following SN2 reaction.
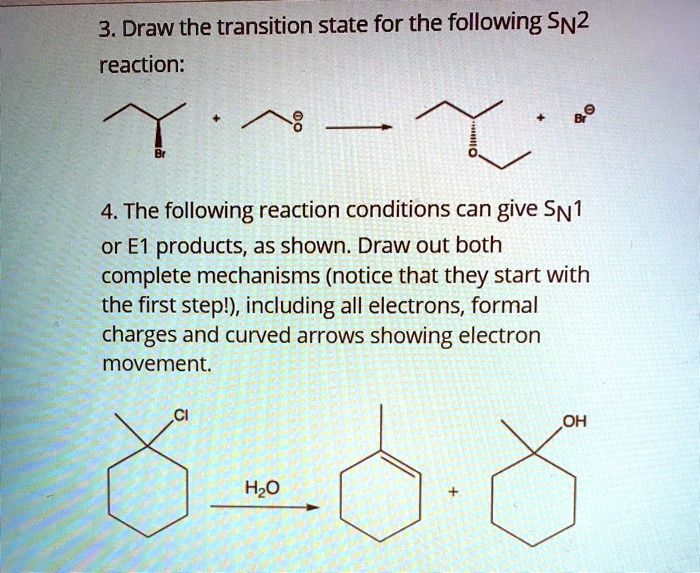
Solved 3 Draw The Transition State For The Following Sn2 Reaction 4 The Following Reaction Conditions Can Give Sni Or E1 Products As Shown Draw Out Both Complete Mechanisms Notice That They Start
Nucleophile 11C 14C k 11 k 14 and secondary alpha-deuterium k H k D alpha kinetic isotope effects KIEs were measured for the S N2 reactions between tetrabutylammonium cyanide and ethyl iodide bromide chloride and tosylate in anhydrous DMSO at 20 degrees C to determine whether these isotope effects can be used to determine the structure of S N2.
. In the transition state of SN2 reaction there are five groups around the carbon and the carbon can be called pentacoordinated. This is called an associative or SN2 mechanism. Indicate bonds which are forming and those which are breaking by dashed lines.
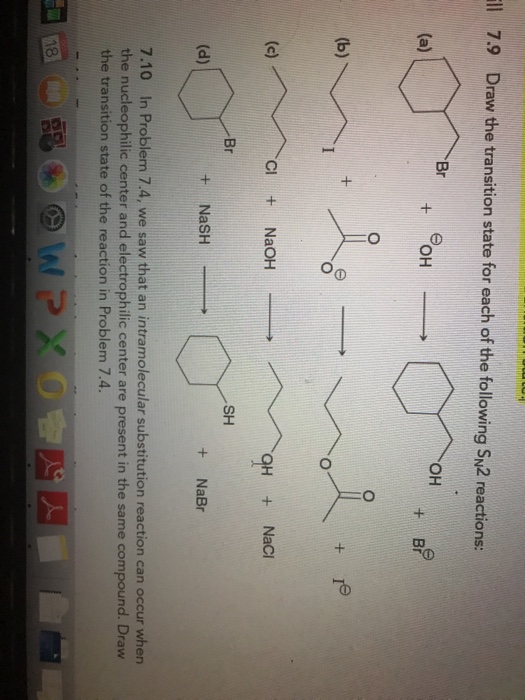
Methyl halide highly reactive primary halide secondary halide β-substituted halide tertiary halide practically unreactive. Draw the Transition state for the following SN2 reaction. As a reminder from the introduction to nucleophilic substitutions these are reactions where the nucleophile replaces the leaving group.
Draw the structure of reactants and products on the diagram. Draw an energy diagram for the following S N 2 reaction. Given the steric and molecular orbital explanations for backside attack explain why the following SN2 reaction does not occur.
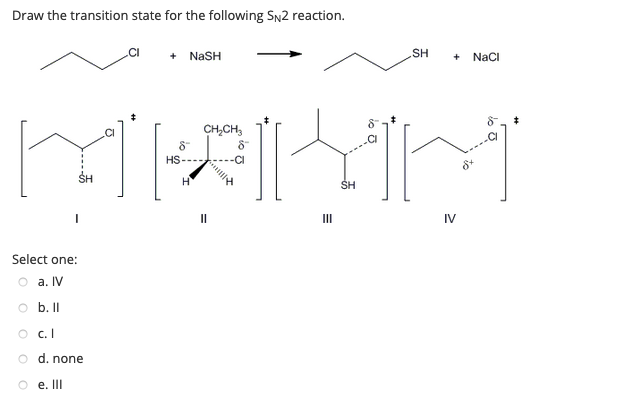
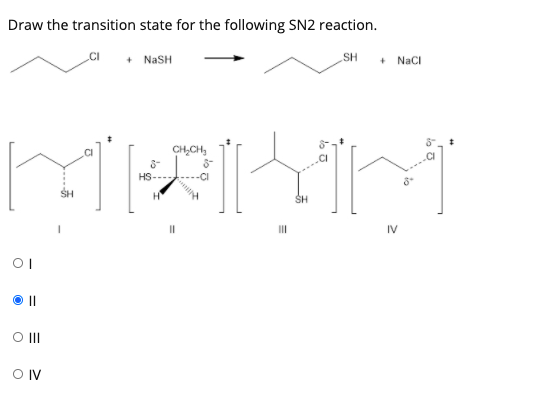
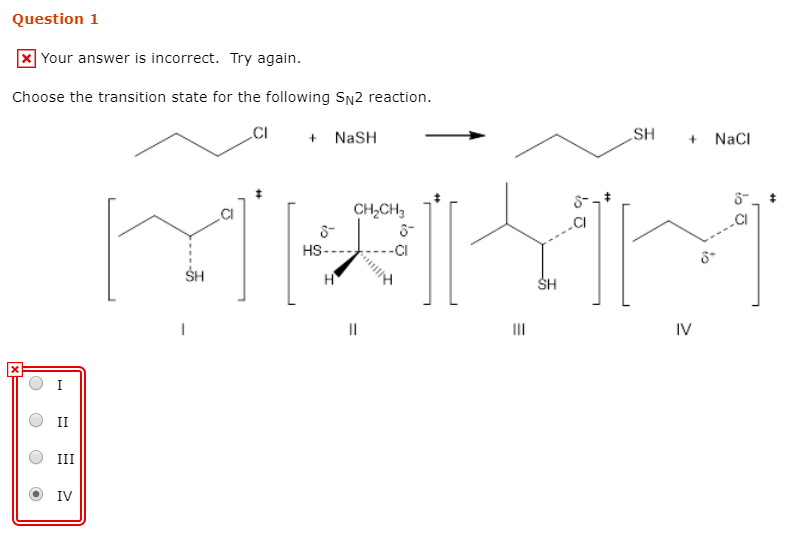
The nucleophile tert -butoxide must get to the σ C-Br antibond for an SN2 reaction to occur. CI NASH SH NaCI CHCH SH IV OII OIV. De A one B.
In a very short transient moment the carbon atom is partially connected with both OH and Br that gives a highest energy level state of the whole process called transition state. Но он ОН Он он ОН ОН НО ОН ОН НО НО НО III IV Question 35 How many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom. In the term S N 2 S stands for substitution the subscript N stands for nucleophilic and the number 2 refers to the fact that this is a bimolecular reaction.
In the first picture S N 2 the reaction takes place in a single step and bond-forming and bond-breaking occur simultaneously. 2 marks H CHZBE. It is my understanding that transition states in an S N 2 reaction have some filled and some empty orbital character as we have the backside of the C-X σ beginning to fill with electrons from the HOMO of the nucleophile forming a C-Nu σ bond in the process.
Set the route card to the following. Up to 256 cash back 23 Sep 2018. If we have an adjacent carbonyl group to the α carbon I have learnt that the TS is then only stabilised by the.
In this mechanism one bond is broken and one bond is formed synchronously ie in one step. P am1 IRCforwardcalcfcmaxpoints300stepsize1recalc10 This means to follow the minimum energy path in the forward see above direction up to 300 points. SN2 is a kind of nucleophilic substitution reaction mechanism the name referring to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism.
3 The leaving group leaves forming the final product. Draw the transition state for the following SN2 reaction. Take the transition state geometry and save it as a new input file MeCl_ts_IRC_forwardgjf and GaussView.
Show all partial charges on appropriate atoms. Question 33 Draw the transition state for the following SN2 reaction. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
Draw the transition state for the reaction. Show how the transition state determines the regio- and stereochemistry in your answer. It also increases the crowding and the energy of the transition state.
Transition state of reaction is a state at which new. Computational study by Pross Shaik 1982 Pross Shaik 1982 seeked to dispel the commonly-held belief that. - NaSH SH NaCl CHCH 8 HS- SH III IV Question 34 The products for the following reaction is.
Assume the reaction is exothermic and ΔH -75 kJmol and Ea 50 kJmol. The rate increases by a factor of 2. Label the axes the Ea the ΔH and the transition state of the reaction.
Draw the transition state for the reaction. Draw and name Stereochemistry. 2 Reaction Transition State SN2 summary.
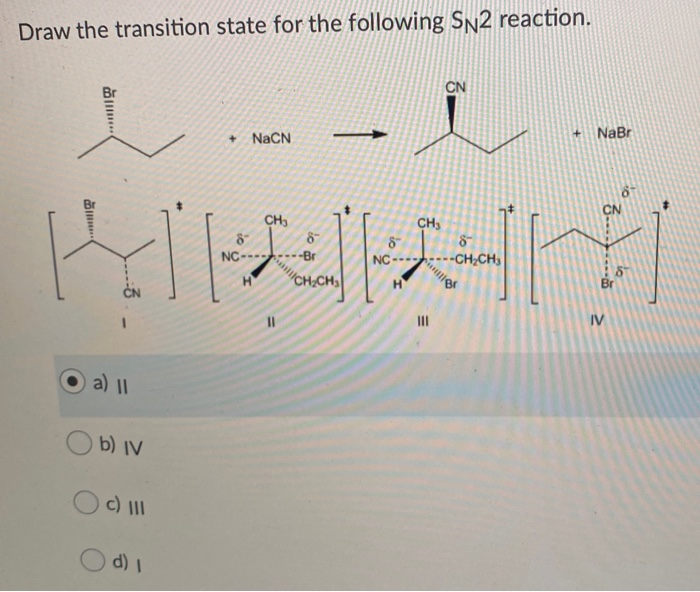
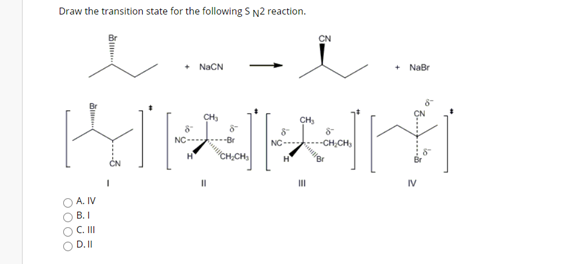
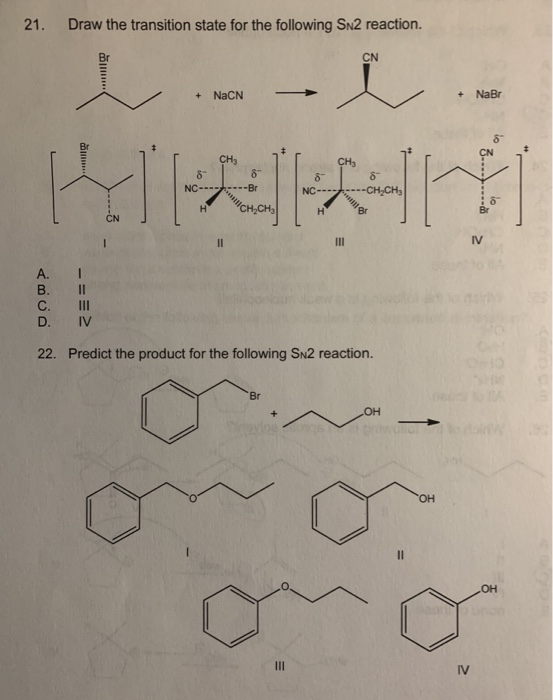
The overall rate depends on a step in which two. 1 Nucleophile back-side attacks the δ carbon center. In the transition state the leaving group Cl- is departing while the nucleophile CN- is forming a bond to the alkyl halide simultaneously.
The alkyl halide is the substrate in the reaction. 2 Transition state forms in which nucleophile is forming bond with carbon while leaving group is breaking its bond. Since two reacting species are involved in the slow step this leads.
The extent of charge development in a transition state is dependent on the earliness or lateness of that transition state. NaSH SH Nal This problem has been solved. For example in the S X N 2 reaction of an anionic nucleophile with a neutral substrate most of the negative charge would.
The cyanide ion attacks the alkyl halide from the rear. Which of the following alkyl halides undergoes the fastest hydrolysis ie. As the OH continues to get closer to the carbon the Br moves further.
These reactions are divided in two main types. Question 5 The Energy Diagram of SN2 reaction. The path to the antibond is blocked by the bulky tert -butyl groups attached to the stereocenter.
NaSH SH Nal Question. C Draw the product Y of the following reaction. CH3I NaCN CH3CN.
The SN2 reaction is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry. One in which the nucleophilic attack and the. The organic product is the nitrile shown in the image attached.
Thus the order of reactivity for an alkyl halide undergoing S N 2 reactions is as follows. CH3I NaCN CH3CN. In this post we will talk about the S N 2 mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Substrate alkyl groups Leaving group. Draw the Transition state for the following SN2 reaction. The reaction of 1-bromopropane with sodium iodide gives 1-iodopropane.
What is the effect of doubling the concentration of NaI on the rate of the reaction. You can put the reactants at any energy level and then draw the. What is the effect of doubling the concentration of NaI on the rate of the reaction.
Solved Draw The Transition State For The Following Sn2 Chegg Com
Answered Draw The Transition State For The Bartleby
Solved Question 1 Your Answer Is Incorrect Try Again Chegg Com
Solved Draw The Transition State For The Following Sn2 Chegg Com
Solved Ll Draw The Transition State For Each Of The Chegg Com

Solved Draw The Transition State For The Following Sn2 Chegg Com
Solved 21 Draw The Transition State For The Following Sn2 Chegg Com
Solved Question 18 4 Points Draw The Transition State For Chegg Com
0 comments
Post a Comment